AMI SQL
Goals
The 3Forge SQL language provides a comprehensive instruction set for working with table(s) of data.
- Retrieval - Accessing and Normalizing data from external sources
- Blending - Perform Joins and Unions on tables
- Modifying - Inserting, Updating, and Deleting rows
- Analyzing - Grouping, Sorting, and Filtering
- Schema Definition - Creating, Updating, and Dropping tables
Broadly speaking, the logic steps involved in data-visualization are:
1. Running a query, or set of queries, on external datasources and/or the AMI-Realtime database.
- Each datasource is predefined and uniquely named.
- The results of queries on datasources will result in temporary, in-memory tables
- The queries can be constructed using user-input/user-selected/user-associated data
- In more advanced cases, the queries can be sequential, meaning the results from one query are then fed into a subsequent query (allowing for reactionary data blending)
2. Blending the results from Step 1, resulting in new temporary in-memory tables 3. Building visualizations on the tables from Step 1 and/or Step 2
AMI SQL and Standard SQL Differences
For those familiar with standard SQL, these are the differences:
1. Equality is done with ==
- AMISQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE userid == 15;
- MYSQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE userid = 15;
2. Checking for null is done with equality, ex. == null
- AMISQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE status == null;
- MYSQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE status IS NULL;
3. Strings are surrounded in double quotes
- AMISQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE name == "David";
- MYSQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE name = "David";
4. "Matches" (~~) instead of LIKE
- AMISQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE name ~~ "^Dav";
- MYSQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE name LIKE "Dav%";
(See Simplified Text Matching for pattern matching rules/expressions)
5. Boolean expressions && works same as AND. || works same as OR
- AMISQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE userid == 15 AND status == null && name == "David";
- MYSQL: SELECT * FROM Users WHERE userid = 15 AND status IS NULL && name = "David";
6. By default all tables are TEMPORARY, use the PUBLIC key word to make non-temporary tables:
- AMISQL: CREATE TABLE MyTemporaryTable(id String);
- AMISQL: CREATE PUBLIC TABLE MyPermanantTable(id String);
Data Source Access Clauses
use...execute_clause
Overview
This command enables you to "execute" code on an external datasource and process/store the results locally
- USE: While datamodels have default options, you can override them for a particular query. Valid options include
- ds = "datasource_name"
- The name of the datasource to execute this script on
- timeout = timeout_in_millis
- The number of milliseconds before the execute command times out
- limit = row_limit_to_return
- The max number of records returned
- ds_url = "url"
- Overrides the url of the datasource
- When used in conjunction with ds="datasource_name", supplied datasource must contain URL in the PermittedOverrides field
- ds_username = "username"
- Overrides the username of the datasource
- When used in conjunction with ds="datasource_name", supplied datasource must contain USERNAME in the PermittedOverrides field
- ds_password = "plain_text_password"
- Overrides the password of the datasource using a plain text password
- When used in conjunction with ds="datasource_name", supplied datasource must contain PASSWORD in the PermittedOverrides field
- Mutually exclusive with the ds_password_enc option
- ds_password_enc = "aes_encrypted_password"
- Overrides the password of the datasource, using an encrypted password
- Use strEncrypt(...) to create an encrypted password
- When used in conjunction with ds="datasource_name", supplied datasource must contain PASSWORD in the PermittedOverrides field
- Mutually exclusive with the ds_password option
- ds_options = "some options"
- Override the options of the datasource
- When used in conjunction with ds="datasource_name", supplied datasource must contain OPTIONS in the PermittedOverrides field
- ds_relay = "relayid"
- Override the relay of the datasource
- Run SHOW RELAYS command and inspect RelayId for available relays
- When used in conjunction with ds="datasource_name", supplied datasource must contain RELAY in the PermittedOverrides field
- ds_adapter = "SOME_ADAPTER"
- Use an "anonymous" datasource of the specified adapter type
- Run SHOW DATASOURCE_TYPES command and inspect the I column for available adapters
- Mutually exclusive with ds="datasource_name" option
- See ami.db.anonymous.datasources.enabled option for permission details
- _custom=some_directive
- Prefixing with an underbar (_) passes the option through to the datasource's adapter
- ds = "datasource_name"
- EXECUTE: The literal text to execute. The text will be sent directly to the datasource for execution. Therefore, variables cannot be referenced. Instead, substitution can be used. See dollarsign_substitution
Syntax
[USE option = value [ option = value ...]] EXECUTE code_to_execute
Example
CREATE TABLE
final_table AS
USE
ds="mydb"
timeout=10000
limit=100
EXECUTE
select * from mytable;
use...show tables clause
Overview
This command enables you to see what tables are available on a given datasource (similar to what the AMI gui wizard shows you when selecting a table).
- USE: While datamodels have default options, you can override them for a particular query. Valid options include
- ds = "datasource_name" The name of the datasource to execute the script on
The resulting table will be called TABLE and contain two String columns: TableName and Schema
Syntax
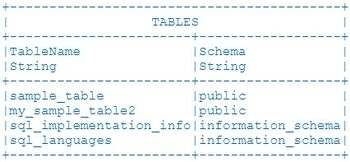
USE ds="mydb" SHOW TABLES;
Example
This example will return a table displaying all tables available in the mydb datasource. If the datasource supports schema names, that will be populated as well.
USE ds="mydb" SHOW TABLES;
//returns:
use...insert clause
Overview
This command uploads data from AMI into a datasource.
- USE: While datamodels have default options, you can override them for a particular query. Valid options include
- ds = "datasource_name" The name of the datasource to execute the script on
The resulting table will be called TABLE and contain two String columns: TableName and Schema
Syntax
USE ds="datasource_name" INSERT [INTO] datasource_table [(col1[, col2 ...])] select_clause
USE ds="datasource_name" INSERT [INTO] datasource_table [(col1[, col2 ...])] analyze_clause
USE ds="datasource_name" INSERT [INTO] datasource_table [(col1[, col2 ...])] prepare_clause
USE ds="datasource_name" INSERT [INTO] datasource_table [(col1[, col2 ...])] execute_clause
USE ds="datasource_name" INSERT [INTO] datasource_table [(col1[, col2 ...])] VALUES values_expr[, values_expr ...]
USE ds="datasource_name" INSERT [INTO] datasource_table [(col1[, col2 ...])] Use_execute_clause
datasource_name - string name of the datasource containing the table to insert values into
datasource_table - name of the table to insert values into
Examples
This example will insert two rows into the mydb datasource's users table:
USE ds="mydb" INSERT INTO users(name,city,state) values ("Rob","NYC","NY"),("Sara","OC","CA");
This example copy all rows from AMI's my_users table into the "mydb" datasource's users table:
USE ds="mydb" INSERT INTO users(name,city,state) SELECT Name,Local,Region FROM my_users;
This example copy all rows from the old_users table in the otherds datasource to the users table in the mydb datasource.
USE ds="mydb" INSERT INTO users(name,city,state) USE ds="otherds" EXECUTE SELECT * FROM old_users
concurrent_block (advanced)
Overview
When running analysis that needs to query many datasources, there can be large performance gains by executing these queries simultaneously. The CONCURRENT{...} key word causes all EXECUTE clauses within the block to be run in parallel (instead of sequentially).
In both of the examples below, we are going to execute three queries on three separate datasources (mydb1, mydb2, mydb3). The first example executes the queries sequentially and the second example executes the queries concurrently.
Assuming each query takes 2 seconds for a database to process, the first example will complete in about 6 seconds (2+2+2), while the second, concurrent, example will complete in only 2 seconds:
Example of Sequential Execution (Default)
{
CREATE TABLE mytable1 AS USE ds="mydb1" EXECUTE select * from mytable;
CREATE TABLE mytable2 AS USE ds="mydb2" EXECUTE select * from mytable;
CREATE TABLE mytable3 AS USE ds="mydb3" EXECUTE select * from mytable;
}
Here is the sequence of events:
00:00:00 - EXECUTE clause is sent to mydb1
00:00:00 - AMI Script sleeps until there is a response from mydb1...
00:00:02 - mytable1 is created (from result of query to mydb1)
00:00:02 - EXECUTE clause is sent to mydb2
00:00:02 - AMI Script sleeps until there is a response from mydb2...
00:00:04 - mytable2 is created (from result of query to mydb2)
00:00:04 - EXECUTE clause is sent to mydb3
00:00:04 - AMI Script sleeps until there is a response from mydb3...
00:00:06 - mytable3 is created (from result of query to mydb3)
00:00:06 - Block is complete after 6 seconds (code after the block will be executed)
Example of Concurrent Execution
So now let's add the CONCURRENT keyword before the block. In this case, all 3 executes will be initiated at the same time.
CONCURRENT{
CREATE TABLE mytable1 AS USE ds="mydb1" EXECUTE select * from mytable;
CREATE TABLE mytable2 AS USE ds="mydb2" EXECUTE select * from mytable;
CREATE TABLE mytable3 AS USE ds="mydb3" EXECUTE select * from mytable;
}
Here is the sequence of events:
00:00:00 - EXECUTE clause is sent to mydb1
00:00:00 - EXECUTE clause is sent to mydb2
00:00:00 - EXECUTE clause is sent to mydb3
00:00:00 - AMI Script sleeps until there is a response from all 3 queries...
00:00:02 - mytable1 is created (from result of query to mydb1)
00:00:02 - mytable2 is created (from result of query to mydb2)
00:00:02 - mytable3 is created (from result of query to mydb3)
00:00:02 - Block is complete after 2 seconds (code after the block will be executed)
Query Clauses
select_clause
Overview
This clause allows the combination of Filtering (WHERE), Sorting (ORDER BY), Aggregating (GROUP BY), Projecting (SELECT …) and Cropping (LIMIT) of individual tables. Next, the results may be combined via Unions (UNION) and/or Joins (FROM … JOIN ON). Complex Strings containing delimited data can be split into distinct rows via the UNPACK operation. Finally, see the create_table_as_clause for storing the final result of a select clause into another table.
- To aggregate data, use the GROUP BY clause to identify any number of columns or derived values that should be used to group rows. Provide an alias (AS) for derived values to be used within the select clause. The select columns can only use aggregate functions (min, max, count, sum) on underlying rows and columns declared in the group-by clause
- To filter data, provide a WHERE clause which evaluates to a Boolean. True indicates don't filter. When filtering in conjunction with aggregating (GROUP BY), those records filtered out will not be considered for aggregation. To filter rows after aggregation, use the HAVING clause.
- For projecting, supply columns to include in the SELECT clause. Derived values may be provided. Provide an alias (AS) for derived values or to rename a column. Use star (*) to include all columns or tblname.* to include only those columns from a particular table provided in the FROM clause.
- To crop out rows, use the LIMIT clause. You may provide a number of rows to skip (offset) and a number of maximum rows to return (rowcount).
- To sort, use the ORDER BY clause. If multiple expressions are given the left-most takes priority.
- To union (concatenate) the results from multiple select clauses, use the UNION clause. The column names and types from the first select clause will provide the result set schema definition. All select clauses participating in a union must define the same number of columns. Note: this operates like a union all in many databases.
- To join (blend) tables, supply all tables together in the FROM clause and a Cartesian product will be provided. For more advanced Joins, you can use a combination of the LEFT, RIGHT, OUTER, JOIN, ON and NEAREST clauses. See JOINING DATA section for details
- To process String columns containing multi-value delimited data, use the UNPACK col ON delimeter expression. This will split the string such that each entry will result in a new row.
Syntax
SELECT column_expr|lambda_expr [, column_expr|lambda_expr ...] FROM table_expr|nested_select_expr [, table_expr|nested_select_expr ...]|
[[LEFT|RIGHT|OUTER] [ONLY] JOIN [table_expr|nested_select_expr] [ON expr] [NEAREST nearest_expr]]
[WHERE where_expr ]
[GROUP BY column_expr [, column_expr ...] [HAVING expr ]]
[ORDER BY expr [ASC|DESC] [, expr [ASC|DESC] ...]]
[UNPACK col_to_unpack ON unpack_delimiter [,col_to_unpack ON unpack_delimiter]]
[LIMIT [offset,] rowcount]
[UNION select_clause]
offset - integer number of rows to skip
rowcount - integer number of maximum rows that will be returned
Joining Data
Simple Cartesian Joins:
Any number of tables can be joined by simply listing them after the FROM clause which will produce a Cartesian product, such that a row will be returned for each possible combination of rows from the source table. For example, the Cartesian product of a table with 5 rows and another table with 3 rows will produce 15 rows (5x3=15). Of course, the WHERE clause can be used to limit results to only the interesting combinations.
Handling Rows that don't match rows in other tables
For more granular control when joining two tables, use the JOIN syntax. There are 7 types of statements, let's assume two tables a and b:
- FULL JOIN: FROM a JOIN b ON expr - This is the same as FROM a,b WHERE expr
- LEFT JOIN: FROM a LEFT JOIN b ON expr - A FULL JOIN plus all records from table a that would otherwise be omitted (due to the expr).
- LEFT ONLY JOIN: FROM a LEFT ONLY JOIN b ON expr - Includes only records from table a that would otherwise be omitted (due to the expr).
- RIGHT JOIN: FROM a RIGHT JOIN b ON expr - A FULL JOIN plus all records from table b that would otherwise be omitted (due to the expr). (similar to LEFT JOIN, swapping a and b)
- RIGHT ONLY JOIN: FROM a RIGHT ONLY JOIN b ON expr - Includes only records from table b that would otherwise be omitted (due to the expr). (similar to LEFT ONLY JOIN, swapping a and b)
- OUTER JOIN: A FULL JOIN plus all records from table a and from table b that would otherwise be omitted (due to the expr
- OUTER ONLY JOIN: Includes only records from table a and from table b that would otherwise be omitted (due to the expr).