GUI
Getting Started
Logging In & The Dashboard
Log into AMI with the provided user name and password (default user/password is demo/demo123)
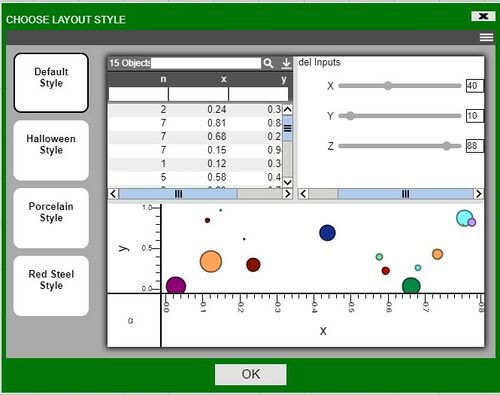
After logging into AMI, choose a layout style (Default Style is shown)
After selecting a style, you will move onto the new dashboard
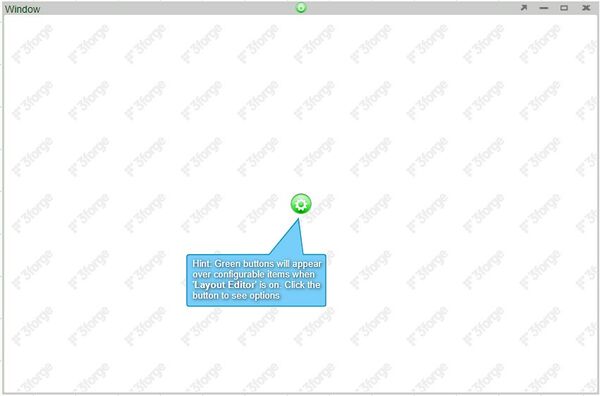
On the dashboard you will see 1) a Layout Editor toggle button in the upper right corner, 2) a menu bar at the top, and 3) the workbook area below where you add layout components
1. Layout Editor Toggle Button
(Hotkey: CTRL + D)
AMI dashboard builder has two modes. When the Layout Editor is turned on, you have access to tools and functionality for editing the dashboard.
Note: if you do not see the Layout Editor Button, your user account is not entitled for building layouts.
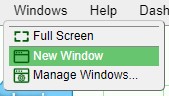
- The Windows menu will have an option to add New Windows and to Manage Windows
- There will be a new Dashboard menu item for accessing tools
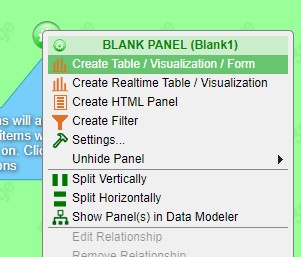
- All existing panels will have a green button for accessing that panel's settings
2. The Menu
- File: manage saving and loading of dashboards
- Account: control your personal settings and preferences
- Windows: access, manage, and create windows
- Help: get AMI version, Runtime settings, and list of available script methods, etc.
- Dashboard (in Layout Editor mode): access tools and functionality for building out the dashboard
(Clicking on the 3Forge icon will open up 3Forge's website in a new tab)
3. The Workbook
This is where the dashboard is presented as it is built or loaded
Creating Your First Visualization
Creating a visualization can be summarized into 3 steps:
1. Create a window to put your visualization in 2. Connect to the data using the Data Modeler 3. Select how you want to visualize your data
Let's demonstrate this by creating a table. Before proceeding,
1. After logging into AMI, enter Layout Editor mode by toggling the Layout Editor mode to ON (found on the upper right corner).
(Hotkey: CTRL + D)
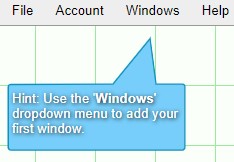
2. The dashboard will now have a grid over the work area and a prompt telling you to click on the Windows menu will appear.
3. Select New Window from the drop down options in order to create a new window with a blank panel
4. Click on the green button in order to access the panel's options and select Create Table/Visualization Form
5. This will open up the visualization wizard. The first step of the wizard is the Data Modeler, which is the primary way of connecting to the data you want to visualize.
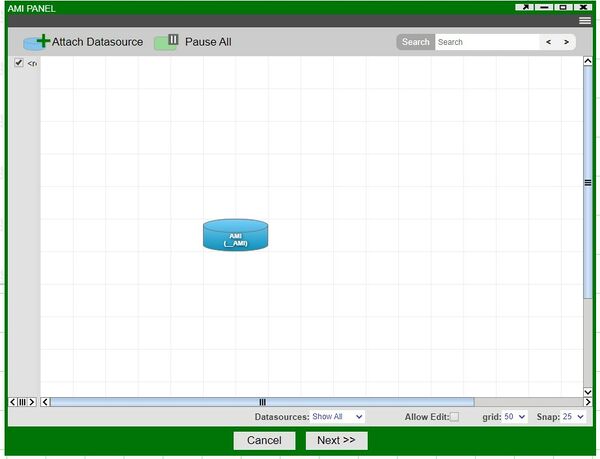
6. At the top of the Data Modeler, click on Attach Datasource in order to connect to a database containing your data. This will open up the Add Datasource window. In our example, we will be connecting to a MySQL database. Fill out the necessary fields and click on the Add Datasource button
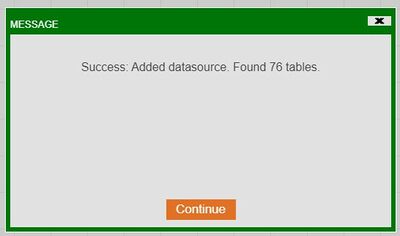
7. A successful connection will show a similar prompt.
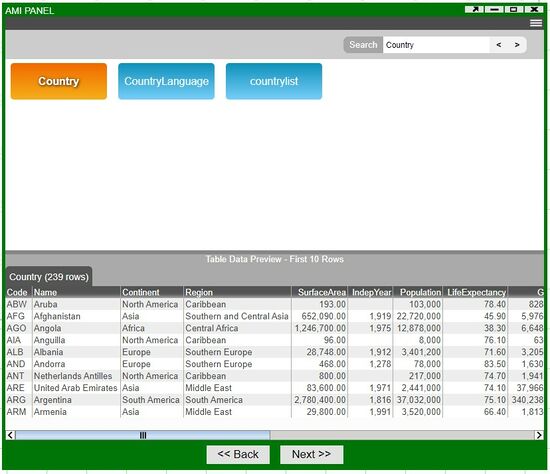
8. Next, you will see all of the tables that are accessible in the datasource. Select the table you would like to visualize. You can use the search function in datasources containing many tables.
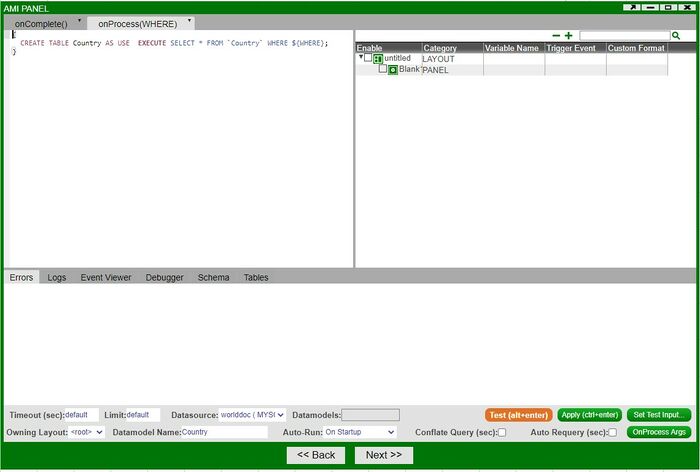
9. You will then be taken to the editing portion of the Data Modeler. Here, you can 'massage' the data in preparation for use in the visualization. If you are ready, click on Test. If everything is working and there are no errors, click on Next.
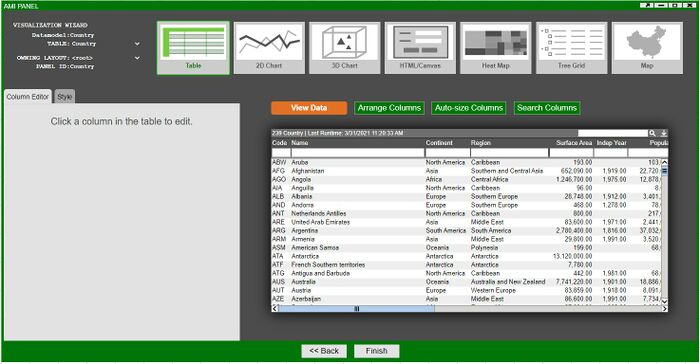
10. In the final portion of the visualization wizard, you will select the kind of visualization you would like to create in the panel. In our example, we will create a table by selecting the Table icon and clicking on Finish.
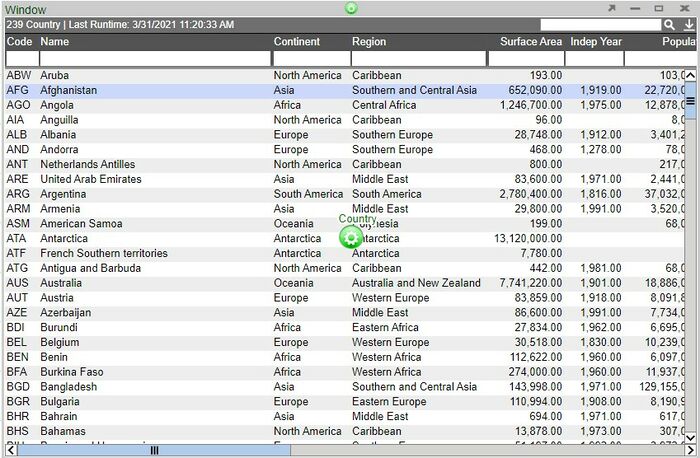
11. In place of a blank panel, we now have our table
In summary - using the visualization wizard, we first created a Datamodel based on a table found in the datasource. We then edited the Datamodel in the Datamodel editor before finally using it to create a table. Many of the topics in this tutorial will be covered in greater detail throughout the GUI documentation.
Creating a Relationship Between Visualizations
Continuing from the previous section, we will build a second visualization and establish a relationship between two panels (two visualizations).
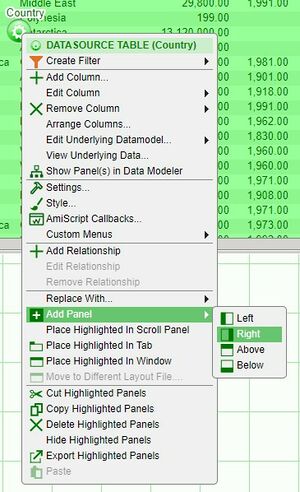
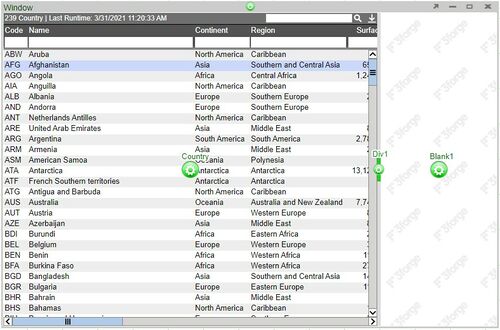
1. Click on the panel configuration button of the created table and select Add Panel > Right in order to create a empty panel to the right side of the table.
Note: use the divider in order to adjust the size of the panels. You can also adjust the size of the window
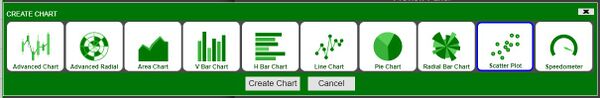
2. Click on the new panel's configuration button and follow the steps of the previous section up to the final step of the visualization wizard. This time, we will select 2D Chart in the wizard
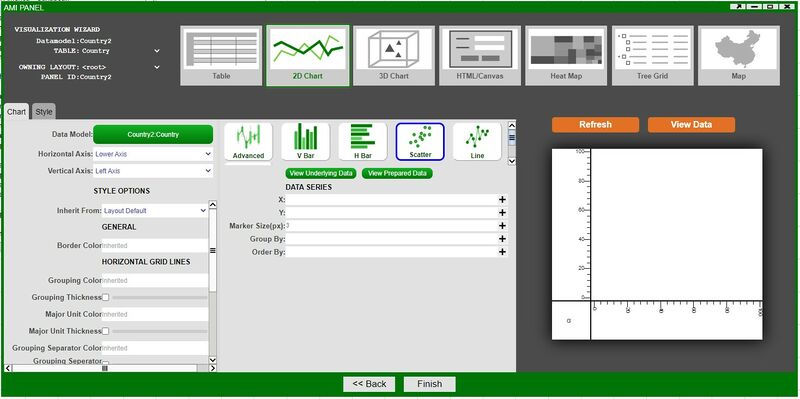
3. Selecting 2D Chart opens up another set of options - select Scatter Plot and then click on Create Chart in order to open the chart wizard
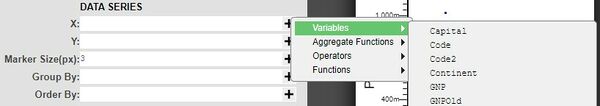
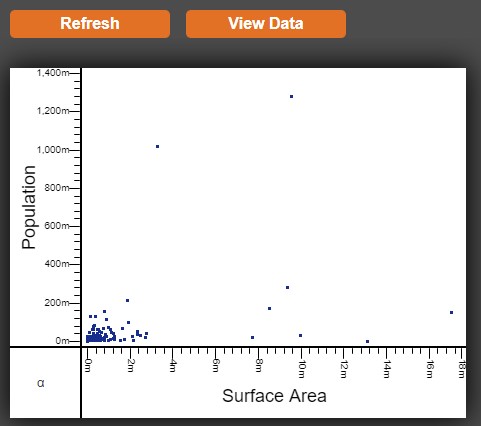
4. Under DATA SERIES, click on the ![]() of the X & Y fields in order to see the variables that can be used. After selecting the desired variables, click on Refresh in order to preview the chart.
of the X & Y fields in order to see the variables that can be used. After selecting the desired variables, click on Refresh in order to preview the chart.
Note: Scatter is one of the ready-made chart options - with many of the fields pre-populated and only requiring X & Y values. Advanced contains all of the options that can be configured on a chart. Adding Labels can be done in the Advanced section.
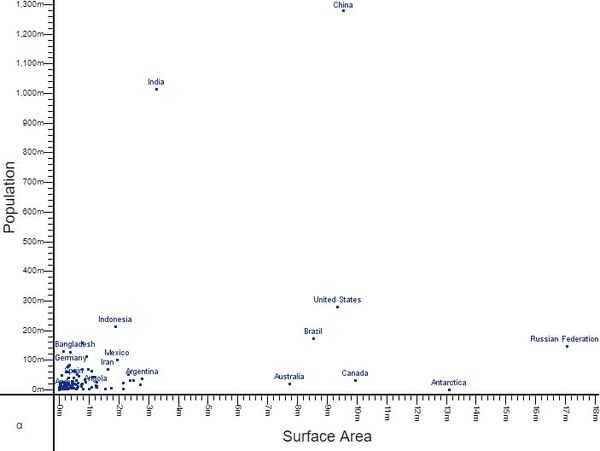
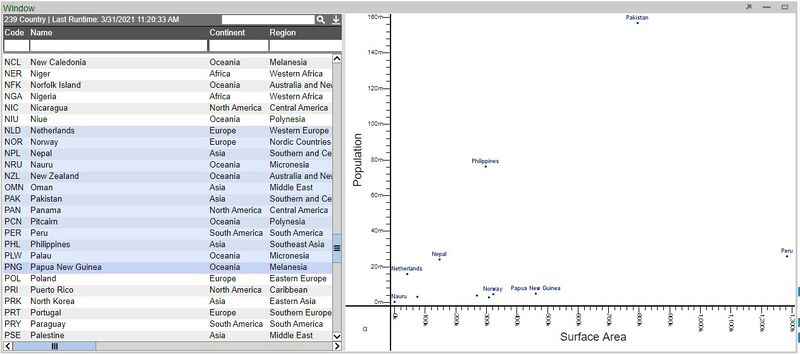
5. Click Finish in order to return to the dashboard and to view the chart.
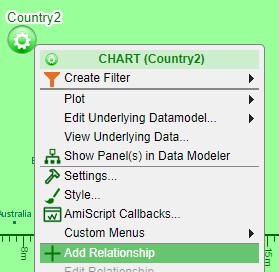
6. AMI allows you to easily correlate the two visualizations by creating a relationship between the two panels - a source and a target. In order to create a relationship, click on the configuration button of the target panel (Country2/chart) and select Add Relationship.
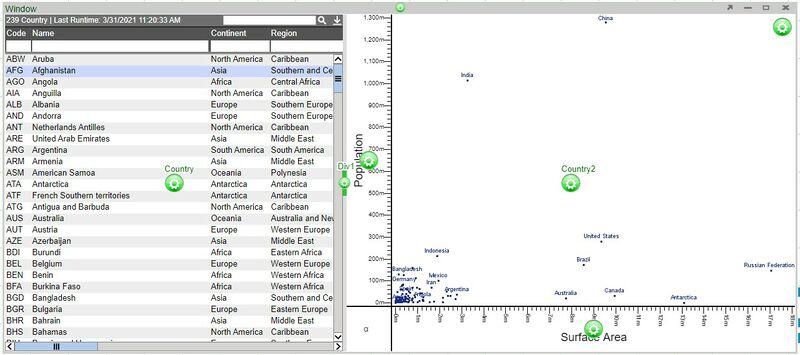
7. An arrow will appear from the configuration button. Move to the source panel (Country/table) and click on the configuration button in order to establish the relationship.
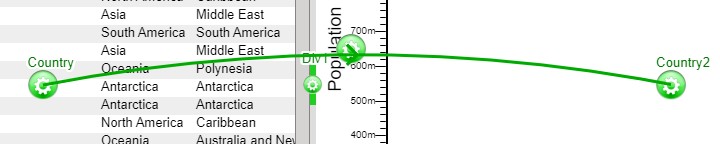
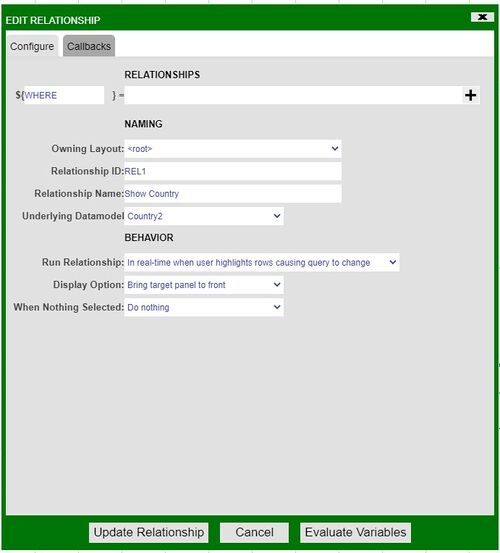
8. Once established, a relationship menu will appear. Use this menu to select the variables that the relationship will use to correlate between the two visualizations. A variable that is available on both visualizations must be used in order to correctly maintain the relationship. In our example, we will use the Code variable found in both tables.
9. With a relationship between the two visualizations, selecting rows from the table will now display correlated points on the scatter plot.
In summary - we established a second panel in a single window and created a chart on this new panel. We then created a relationship between the table and the chart in order to show a correlation between the two visualizations.
Handling relationship between two panels driven by non-AMI Database data models
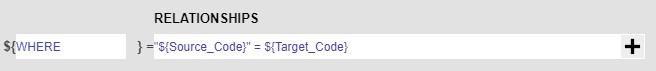
Note that if you are creating a relationship between two panels whose underlying data models' datasource is non-AMI, you have to manually add ${WHERE} to the end of your where (or the equivalent in that database's syntax) statement. For example, running a relationship between two Oracle powered data model requires additional input in the format of where ${WHERE} or where CONDITION1 and/or ${where}, etc...
Moreover, in the relationship field, you must adhere to the syntax of the non-AMI database for the use of quotes for string. For example, AMI database uses double quotes for string, but Oracle DB mandates single quotes.
Styles
For any visualizations, you can click on the green setting button and access the styling options for that panel by clicking Style. Also in that style section, you can click on the names of the styles and a code will show up. You can set the style programmatically in the datamodeler or in any AMI callbacks by first calling getStyleSet() on any panel object, assign it to a variable, then use the styleSet's setValue(string code, string value) method to set the style.
Ex:
styleset ss = myTablePanel.getStyleSet();
ss.setValue("tableFontFm", "Courier"); // returns true/false.
Style Codes for AMISCRIPT
Here is a complete list of style codes that you may use in an AMI editor or callbacks:
Code prefix:
Table -> table
2D Chart -> chart
3D Chart -> chart3d
HTML panel -> form
Tree -> treegrid
Map -> map
Cell (table)/Body (treegrid)
Ex: tableFontFm/treegridFontFm
Font = FontFm
Background color = BgCl
Label/Font Color = FontCl
Row Height = RowHt
Font Size = FontSz
Gray Bar Color = GraybarCl
Bottom Border/ Cell Bottom Border = CellBtmPx
Right Border/ Cell Right Border = CellRtPx
Border Color/ Cell Border Color = CellBdrCl
Cell Horizontal Padding = CellPadHt
Vertical Align = VtAlign
Values (chart)
Font = chartFontFam
Font Style = chartFontSt
Background Color = chartBgCl
Selected Color = chartSelCl
Select Box Color = chartSelBoxCl
Selection Box Border Color = chartSelBoxBrdCl
Divider Color = chartDivCl
Horizontal Divider Size = chartDivThckH
Vertical Divider Size = chartDivThckV
Options Slider Fields Color = chartScrCl
Partition Colors = chartSeriesCls
Gradient Colors = chartGradient
General (chart3d)
Background Color = chart3dBgCl
Selection Color = chart3dSelCl
Label Color = chart3dFontCl
Control Button Color = chart3dCtrlBtnsCl
Control Buttons = chart3dHideCtrls
Column Header (table)
Background Color = tableHeaderBgCl
Font Color = tableHeaderFontCl
Height = tableHeaderHt
Font Size = tableHeaderFontSz
Hide Divider = tableHeaderDivHide
Column Filters (table/treegrid)
Hide Column Filters = ColumnFilterHide
Height = ColumnFilterHeight
Background Color = ColumnFilterBgCl
Font Color = ColumnFilterFontCl
Font Size = ColumnFilterFontSz
Border Color = ColumnFilterBdrCl
Selection (table/treegrid)
Selected Color = SelCl
Active Color = ActCl
Search Bar (table)
Hide = tableSearchHide
Divider Color = table SearchBarDivCl
Background Color = tableSearchBgCl
Font Color = tableSearchFontCl
Search Field Color = tableSearchFldCl
Search Field Border Color = tableSearchFldBdrCl
Search Field Font Color = tableSearchFldFontCl
Button Color = tableSearchBtnsCl
Search Bar (treegrid)
Hide = treegridSearchHide
Background Color = treegridSearchBgCl
Search Field Font Color = treegridSearchFldFontCl
Search Field Border Color = treegridSearchFldBdrCl
Button Color = treegridSearchBtnsCl
Filtered Header (table/treegrid)
Background Color = FiltBgCl
Font Color = FiltFontCl
Style (form)
Font Color = formFontCl
Background Color = formBgCl
Show Buttons Panel = formShowBtmBtns
Field (form)
Background Color = formFldBgCl
Font Color = formFldFontCl
Font Family = formFldFontFam
Font Size = formFldFontSz
Primary Color = formFldPrimCl
Secondary Color = formFldSecCl
Border Color = formFldBdrCl
Label (form)
Label Padding = formLblPd
Font Size = formFontSz
Text Alignment = formTxtAlign
Rotate HTML = formRotate
Font Family = formFontFam
Is Bold = formBold
Is Italic = formItalic
Is Underline = formItalic
Show Label = formFldLblStatus
Side = formFldLblSide
Alignment = formFldLblAlign
Field CSS (form)
Checkbox = formFldCssCheck
Date = formFldCssDate
Daterange = formFldCssDateRng
Datetime = formFldCssDateTime
Div = formFldCssDiv
Button = formFldCssBtn
Image = formFldCssImg
Multiselect = formFldCssMultiSel
Range = formFldCssRng
Select = formFldCssSel
SubRange = formFldCssSubRng
TextArea = formFldCssTxtArea
Text = formFldCssTxt
Time = formFldCssTime
Timerange = formFldCssTimeRng
Upload = formFldCssUpload
Font Family (heatmap)
Font Family = heatmapFontFam
Grouping (heatmap)
Font Size = heatmapGroupFontSz
Font Color = heatmapGroupFontCl
Border Size = heatmapGroupBdrSz
Border Color = heatmapGroupBdrCl
Background Color = heatmapGroupBgCl
Nodes (heatmap)
Font Size = heatmapNodeFontSz
Font Size = heatmapNodeFontCl
Border Size = heatmapNodeBdrSz
Border Color = heatmapNodeBdrCl
Color Gradient = heatmapNodeGradient
Alignment = heatmapTxtAlign
Vertical Alignment = heatmapVtAlign
Select (heatmap)
Border Color 1 = heatmapSelBdrCl1
Border Color 2 = heatmapSelBdrCl2
Header (treegrid)
Hide Header Bar = treegridHeaderBarHide
Hide Divider Bar = treegridHeaderDivHide
Background Color = treegridHeaderBgCl
Font Color = treegridHeaderFontCl
Header Height = treegridHeaderHt
Font Size = treegridHeaderFontSz
Scroll Bar Colors (chart3d)
X Color = chart3dScrXCl
Y Color = chart3dScrYCl
Z Color = chart3dScrZCl
Zoom Color = chart3dScrZoomCl
FOV Color = chart3dScrFOVCl
X Position Color = chart3dScrXPosCl
Y Position Color = chart3dScrYPosCl
Partition Colors = chart3dSeriesCls
Gradient Colors = chart3dGradient
Selection Box (map)
Color = mapboxSelCl
Border Color = mapboxSelBdrCl
ScrollBar Options (table, chart3d, form, treegrid)
Ex: tableScrollWd
Width = ScrollWd
Grip Color = ScrollGripCl
Track Color = ScrollTrackCl
Button Color = ScrollBtnCl
Icons Color = ScrollIconsCl
Border Color = ScrollBdrCl
Visualization Title (table/chart3d/chart/form/treegrid/map)
Ex: tableTitlePnlFontFm
Font = TitlePnlFontFm
Font Size = TitlePnlFontSz
Alignment = TitlePnlAlign
Title Color = TitlePnlFontCl
Visualization Padding (table/chart3d/chart/form/treegrid/map)
Ex: tablePdLfPx
Left = PdLfPx
Right = PdRtPx
Top = PdTpPx
Bottom = PdBtmPx
Top-Left Radius = PdRadTpLfPx
Top-Right Radius = PdRadTpRtPx
Bottom-Left Radius = PdRadBtmLfPx
Bottom-Right Radius= PdRadBtmRtPx
Color = PdCl
Visualization Shadow (table/chart3d/chart/form/treegrid/map)
Ex: chart3dPdShadowHzPx
Horizontal = PdShadowHzPx
Vertical = PdShadowVtPx
Size = PdShadowSzPx
Color = PdShadowCl
Visualization Border (table/chart3d/chart/form/treegrid/map)
Ex: formPdBdrSzPx
Size = PdBdrSzPx
Color = PdBdrCl