Difference between revisions of "Introduction to AMI"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | = Overview = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
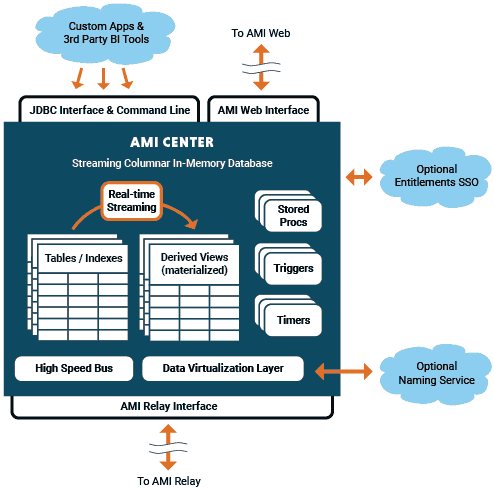
The AMI platform is a comprehensive suite of testing changes components designed to provide a consolidated view across all the various applications and IT resources within large information technology environments. It has interfaces and adapters for interacting with the most expansive technology environments. | The AMI platform is a comprehensive suite of testing changes components designed to provide a consolidated view across all the various applications and IT resources within large information technology environments. It has interfaces and adapters for interacting with the most expansive technology environments. | ||
| − | + | [[File:IntroAMI.1.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Components== | ||
AMI has 5 key components: | AMI has 5 key components: | ||
| − | * '''Webserver''' - AMI's self-contained webserver is used for hosting the dashboard builder tool as well as the dashboards themselves. The webserver is specially designed for supporting real-time AJAX enabling fast and efficient data visualization and interaction. | + | *'''Webserver''' - AMI's self-contained webserver is used for hosting the dashboard builder tool as well as the dashboards themselves. The webserver is specially designed for supporting real-time AJAX enabling fast and efficient data visualization and interaction. |
| − | * '''In-Memory Database''' - The in-memory relational database stores system configurations and custom data. It is a full-featured SQL-based database with specialized features for data analysis, machine learning and event processing. All data is accessible from dashboards in real-time - meaning that changes to the data can be viewed in real-time from the front-end without refreshing or re-running queries. External applications can also use the JDBC interface for querying and mutating the database. | + | *'''In-Memory Database''' - The in-memory relational database stores system configurations and custom data. It is a full-featured SQL-based database with specialized features for data analysis, machine learning and event processing. All data is accessible from dashboards in real-time - meaning that changes to the data can be viewed in real-time from the front-end without refreshing or re-running queries. External applications can also use the JDBC interface for querying and mutating the database. |
| − | * '''Event Processing System''' - AMI supports | + | *'''Event Processing System''' - AMI supports real-time high-speed streaming of data into its core in-memory database. As data streams in, it can be processed by filters, triggers, timed jobs and more. The resulting data can be viewed in real-time through the dashboard. Additional events can be generated when event sequences are processed accordingly. |
| − | * '''Data Virtualization''' - Any number of databases, remote file systems and custom processes can be passively attached to AMI. These attached "datasources" can then be queried by AMI. Queries are invoked either via the event processing system, scheduled timers and/or user solicited actions such as mouse clicking on a row or button. Queries can be executed across multiple datasources simultaneously with results being blended. This virtualization layer can also be used to upload data. | + | *'''Data Virtualization''' - Any number of databases, remote file systems and custom processes can be passively attached to AMI. These attached "datasources" can then be queried by AMI. Queries are invoked either via the event processing system, scheduled timers and/or user solicited actions such as mouse clicking on a row or button. Queries can be executed across multiple datasources simultaneously with results being blended. This virtualization layer can also be used to upload data. |
| − | * '''Plugin Management''' - AMI supports a variety of plugins at various touch points throughout the platform. Plugins are loaded into the JVM at startup by referencing the plugins' class names in the appropriate properties. | + | *'''Plugin Management''' - AMI supports a variety of plugins at various touch points throughout the platform. Plugins are loaded into the JVM at startup by referencing the plugins' class names in the appropriate properties. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==External Interfaces== | |
| + | There are 8 key categories of external interfaces supported by AMI: | ||
| − | + | *'''GUI''' - Fully featured dashboards can be built to provide user access to all the various components and data made available to AMI. AMI utilizes the standard web browser (http[s]) for constructing and using dashboards as well as most of the administration and configuration. | |
| − | + | *'''Queries''' - You can attach to any number of datasources to AMI and query them at runtime - either by a user action or by some electronic/automated event. This feature is core to the "leave the data where it is" concept. For example, you could attach to a database such that users could click on an account to query for its details. | |
| − | + | *'''Real-time Streaming''' - Applications can connect to AMI's real-time interface and stream messages directly into AMI. These can include sending new records or updating or deleting existing records. This can be used to push information onto dashboards in real-time and/or to evaluate events with AMI's event processing system. | |
| + | *'''Callbacks''' - Applications can register call backs with AMI. These callbacks can be executed by the user or automatically triggered by AMI's event processing system. | ||
| + | *'''JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)''' - AMI can be accessed via JDBC just like accessing other traditional databases. JDBC can be used to query and/or update the internal state of AMI. In combination with AMI's data virtualization layer, this can also be used to query multiple datasources using a common JDBC connection. | ||
| + | *'''Command Line''' - The command line interface allows users and/or applications to connect directly into AMI's backend and run commands. | ||
| + | *'''Trace Level Exhaust''' - All mutations to AMI's internal state are made available through the trace level exhaust. This is used for persisting data and auditing changes. | ||
| + | *'''Enterprise I/O''' - Most enterprises have existing operations environments consisting of single sign on services, Entitlements/User Permissions and Naming services. AMI has interfaces at key touch points throughout for providing adapters into the existing infrastructure. | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 13 April 2021
Overview
The AMI platform is a comprehensive suite of testing changes components designed to provide a consolidated view across all the various applications and IT resources within large information technology environments. It has interfaces and adapters for interacting with the most expansive technology environments.
Components
AMI has 5 key components:
- Webserver - AMI's self-contained webserver is used for hosting the dashboard builder tool as well as the dashboards themselves. The webserver is specially designed for supporting real-time AJAX enabling fast and efficient data visualization and interaction.
- In-Memory Database - The in-memory relational database stores system configurations and custom data. It is a full-featured SQL-based database with specialized features for data analysis, machine learning and event processing. All data is accessible from dashboards in real-time - meaning that changes to the data can be viewed in real-time from the front-end without refreshing or re-running queries. External applications can also use the JDBC interface for querying and mutating the database.
- Event Processing System - AMI supports real-time high-speed streaming of data into its core in-memory database. As data streams in, it can be processed by filters, triggers, timed jobs and more. The resulting data can be viewed in real-time through the dashboard. Additional events can be generated when event sequences are processed accordingly.
- Data Virtualization - Any number of databases, remote file systems and custom processes can be passively attached to AMI. These attached "datasources" can then be queried by AMI. Queries are invoked either via the event processing system, scheduled timers and/or user solicited actions such as mouse clicking on a row or button. Queries can be executed across multiple datasources simultaneously with results being blended. This virtualization layer can also be used to upload data.
- Plugin Management - AMI supports a variety of plugins at various touch points throughout the platform. Plugins are loaded into the JVM at startup by referencing the plugins' class names in the appropriate properties.
External Interfaces
There are 8 key categories of external interfaces supported by AMI:
- GUI - Fully featured dashboards can be built to provide user access to all the various components and data made available to AMI. AMI utilizes the standard web browser (http[s]) for constructing and using dashboards as well as most of the administration and configuration.
- Queries - You can attach to any number of datasources to AMI and query them at runtime - either by a user action or by some electronic/automated event. This feature is core to the "leave the data where it is" concept. For example, you could attach to a database such that users could click on an account to query for its details.
- Real-time Streaming - Applications can connect to AMI's real-time interface and stream messages directly into AMI. These can include sending new records or updating or deleting existing records. This can be used to push information onto dashboards in real-time and/or to evaluate events with AMI's event processing system.
- Callbacks - Applications can register call backs with AMI. These callbacks can be executed by the user or automatically triggered by AMI's event processing system.
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) - AMI can be accessed via JDBC just like accessing other traditional databases. JDBC can be used to query and/or update the internal state of AMI. In combination with AMI's data virtualization layer, this can also be used to query multiple datasources using a common JDBC connection.
- Command Line - The command line interface allows users and/or applications to connect directly into AMI's backend and run commands.
- Trace Level Exhaust - All mutations to AMI's internal state are made available through the trace level exhaust. This is used for persisting data and auditing changes.
- Enterprise I/O - Most enterprises have existing operations environments consisting of single sign on services, Entitlements/User Permissions and Naming services. AMI has interfaces at key touch points throughout for providing adapters into the existing infrastructure.